Download FREE Handwritten Notes in PDF Format of Chapter 9: Psychology and Sports Class 12 Notes NCERT Physical Education in English. Size of the given PDF is 2.5 MB and Total Pages in the PDF are 7. These notes are helpful in Acing class 12th board exams and other exams where physical education is required. You don’t have to pay any charges or worry about bugs, viruses. We support, you learn.
Imagine a sprinter at the starting line, heart racing, mind focused, every muscle ready to explode into action. Or a cricketer facing the last ball, the match hanging by a thread. In these moments, success isn’t just about physical ability—it’s about psychology.
Details of Chapter 9: Psychology and Sports Class 12 Notes | NCERT Physical Education Handwritten Notes
- Subject: Physical Education
- Chapter: 9 Psychology and Sports
- Size: 2.5 MB
- Total Pages: 7
- Language: English
- Format: PDF
- Download link: Scroll down below to find download link.
Preview and Download Link of Chapter 9: Psychology and Sports Class 12th Physical Education Handwritten Notes PDF
Here’s a Preview of Handwritten Notes PDF to check before Downloading.
Images Chapter 9: Psychology and Sports Class 12th Physical Education Handwritten Notes PDF
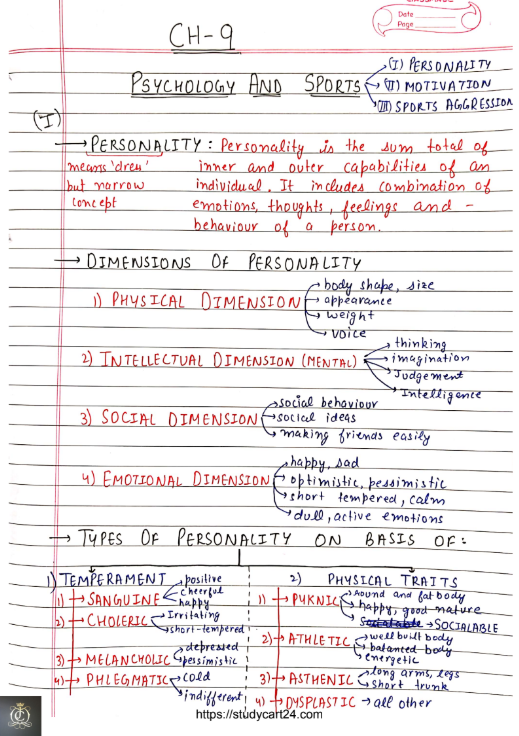



Related Notes: Chapter 2 Sports and Nutrition Class 12 Notes PDF Physical Education Handwritten Notes
Other Recommended Study Material From AMAZON
🙏 Support Our Work
We work very hard to create quality handwritten notes to support your learning journey. Every page is the result of hours of dedication and care. If you find our efforts valuable, please consider supporting us. Even a small contribution of ₹5, ₹10, ₹50, or ₹100 — whatever feels right to you — can make a big difference. Your support helps us continue this platform and keep the notes accessible to everyone. Donate securely via PhonePe – your kindness truly means a lot.
UPI ID:
(Tap to copy)
Please Donate ₹5, ₹10, ₹50, ₹100 or whatever feels right to you.
Key Concepts in Chapter 9: Psychology and Sports Physical Education Class 12th NCERT
1. Motivation: The Driving Force
- Motivation is what pushes an athlete to train harder, wake up early, and keep going despite setbacks. It can be:
- Intrinsic Motivation: Driven by passion, enjoyment, or personal satisfaction.
- Extrinsic Motivation: Influenced by rewards, recognition, or social approval.
- Example: Cristiano Ronaldo’s relentless drive to improve stems from both intrinsic (love for football) and extrinsic (winning trophies) motivation.
2. Personality and Sports Performance
- Different personality types impact an athlete’s approach:
- Extroverts: More social, team-oriented, and thrive in competitive environments (e.g., football players).
- Introverts: Prefer solo sports requiring focus (e.g., chess, archery).
- Example: Serena Williams’ confident and aggressive personality plays a huge role in her dominance in tennis.
3. Aggression in Sports
- Controlled aggression can be beneficial, but excessive aggression can lead to penalties or injuries.
- Example: A footballer using controlled aggression to win a tackle versus unnecessary fouls due to anger.
4. Stress and Anxiety Management
- Anxiety before a big game is normal, but too much can hurt performance.
- Techniques like deep breathing, visualization, and positive self-talk help manage stress.
- Example: Indian cricket captain MS Dhoni remained calm under pressure, earning him the nickname “Captain Cool.”
5. Goal Setting for Athletes
- SMART Goals: Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound.
- Example: Instead of “I want to run faster,” a SMART goal is “I will reduce my 100m sprint time by 0.5 seconds in three months.”
6. Mental Imagery and Visualization
- Athletes imagine themselves succeeding to boost confidence and focus.
- Example: Michael Phelps visualized every possible race scenario before competing in the Olympics.
7. Team Cohesion and Leadership
- Strong teams rely on communication, trust, and leadership.
- Example: Lionel Messi’s leadership on and off the field unites Argentina’s national football team.
Real-Life Examples: The Power of Psychology in Sports
- Kobe Bryant’s Mamba Mentality: Focus, resilience, and an unbreakable work ethic.
- Usain Bolt’s Confidence: A relaxed mind and self-belief helped him dominate sprinting.
- Sachin Tendulkar’s Concentration: Ability to focus under immense pressure for decades.
Mock Questions – Chapter 9: Psychology and Sports Class 12th
- Define sports psychology and its significance in athletic performance.
- Explain the difference between intrinsic and extrinsic motivation with examples.
- How does personality influence sports performance?
- Describe two stress management techniques for athletes.
- What are SMART goals? Provide an example related to sports.
Important Topics of Chapter 9: Psychology and Sports
- Role of psychology in sports
- Motivation and goal setting
- Stress, anxiety, and coping mechanisms
- Team dynamics and leadership
- Mental toughness and resilience
FAQs: Psychology and Sports Class 12 Notes
You can download the PDF notes below from Download and preview section.
Focus on key concepts, practice mock questions, and revise regularly.
Use flashcards, mind maps, and group discussions for better retention.
Not understanding real-life applications, memorizing without grasping concepts, and neglecting mock tests.
Practice relaxation techniques like deep breathing, take breaks, and stay confident.
Conclusion: Psychology and Sports Class 12th
Sports are not just about physical strength; they are also about mental fortitude. Athletes who understand psychology can improve performance, handle pressure, and stay motivated. Whether you’re a student, an aspiring athlete, or a sports enthusiast, mastering these psychological principles will help you in both sports and life.
Tags: Studycart24 Free handwritten notes,
Class 12th NCERT Easy REVISION NOTES,
Physical Education NCERT Notes
Chapter 9 Psychology and Sports Notes,
Handwritten Notes PDF for Class 12 PE,
Physical Education Board Exam Notes,
Psychology and Sports Revision Notes,
Class 12 Physical Education Important Questions,
CBSE Class 12 PE Notes PDF,
Best Notes for Class 12 PE Exam,
NCERT Physical Education Chapter 9 Summary,
PE Class 12 Board Exam Preparation,
Free Download PE Handwritten Notes,
12th Board Physical Education Study Material,
Psychology and Sports Class 12 Notes


